Open finance is one of my favourite topics in recent months of its potential growth and how the importance of its future.
What are Open Finance and its benefit that shape the financial industry?
Firstly, Open finance refers to a financial system where financial services, products, and data are made available and accessible to everyone, regardless of their location, income, or financial status. Open finance enables the creation of new financial products and services that are more inclusive, transparent, and secure than traditional financial services.

There are 3 key benefits that open finance in centralized platforms can bring, including:
- Increased access to financial services
Open finance in centralized platforms can increase access to financial services, especially for people that are neglected by traditional finance, by providing more affordable and accessible financial products and services.
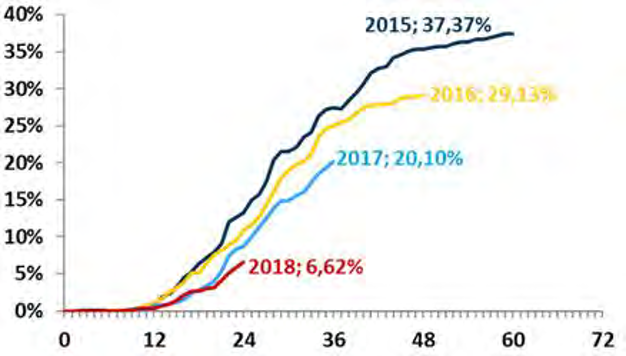
Even the slightest use of innovative data approaches can pose benefits to financial institutions and their clients alike. For example, the use of an online psychometric questionnaire in the loan application process within a portfolio of self-employees, thin file customers in a European retail bank showed that the use of non-traditional data may be, at the same time, credit inclusive and a booster for the credit model accuracy, leading to dramatically lowering default rates. As you can see in the chart below, write-off rates before the scoring deployment (2015 and 2016) were 30–37% and after the deployment (2017 and 2018), the write-off rates hovered at 6–8%.
2. Improved security and more transparency
Centralized open finance applications can leverage advanced security technologies, such as encryption and multi-factor authentication, to protect users’ financial information and assets. Centralized open finance applications can offer greater transparency, as transactions and financial data are stored on a public ledger that all market participants can access.
3. Faster transactions while lower costs
Centralized open finance applications can process transactions much faster than traditional financial institutions, as they can employ cutting-edge digital platforms and blockchain technology. On the other hand, open finance in centralized platforms can offer lower costs compared to traditional financial services, as their extensive use of technology and ‘tech-first’ approach reduces overhead costs and pass savings onto users.
All in one, these 3 key benefits combined are not just helping financial services improve overall user experience. They also enable the creation of more competitive products. Rich and accessible data create more opportunities, which can lead to better financial products and services for consumers.
What is the latest trend in Open Finance and what does the future look like?
The future for open finance is very promising, as it has the potential to bring many benefits to consumers and the financial sector. Some key trends and developments that are likely to shape the future of open finance include:
1. Integration with traditional finance and massive adoption
Open finance is likely to continue to grow in popularity, as more consumers and businesses adopt financial products and services that are based on open finance principles. One of the first waves for open finance is how likely it is to be integrated with traditional finance, as financial institutions and regulators recognize the benefits of open finance and look to leverage it to create new and innovative financial products and services.
Let's look at Robinhood as a centralised platform example for using open finance principles:
Decentralized transactions: Robinhood allows users to make transactions directly on the platform, bypassing the need for intermediaries such as traditional banks. This reduces the cost and time involved in traditional financial transactions and increases the efficiency of the process.
Open APIs: Robinhood provides open APIs to developers, allowing them to build custom applications that integrate with the platform. This allows users to access financial services and products through various channels, making it easier to manage their finances.
Cryptocurrency trading: Robinhood allows users to trade cryptocurrencies as well as traditional assets, such as stocks and ETFs. This expands the financial services available to users and offers them greater flexibility in how they manage their investments.
Robinhood uses open finance principles to make financial services more accessible, efficient, and cost-effective for its users.

One of the most frequent open finance applications is account aggregation meaning that customers can see multiple accounts from different providers on one interface (Plaid, Tink).
Also, open finance can speed up loan approval through instant risk assessment. This is enabled by platforms providing access to client data from different banks (Zip Pay, Klarna). These services contributed to a surge in the popularity of ‘Buy now pay later’ services.
There are quite a few other successful examples of centralized platforms that use the open finance concept to different extents, such as Paypal, Coinbase or Square (embracing open finance principles by providing a platform for users to buy, sell, and hold crypto assets, and by offering small business loans). These, and many more such examples prove the open finance potential.
Also, another reason why open finance is likely to be integrated with traditional finance such as improving security*.*
Centralized platforms that implement open finance can use advanced security measures, such as encryption and multi-signature transactions, to secure user funds and prevent fraud.
2. Regulation
Regulation is likely to play a key role in shaping the future of open finance, as governments and regulators look to balance the benefits of open finance with the need to protect consumers and maintain financial stability.
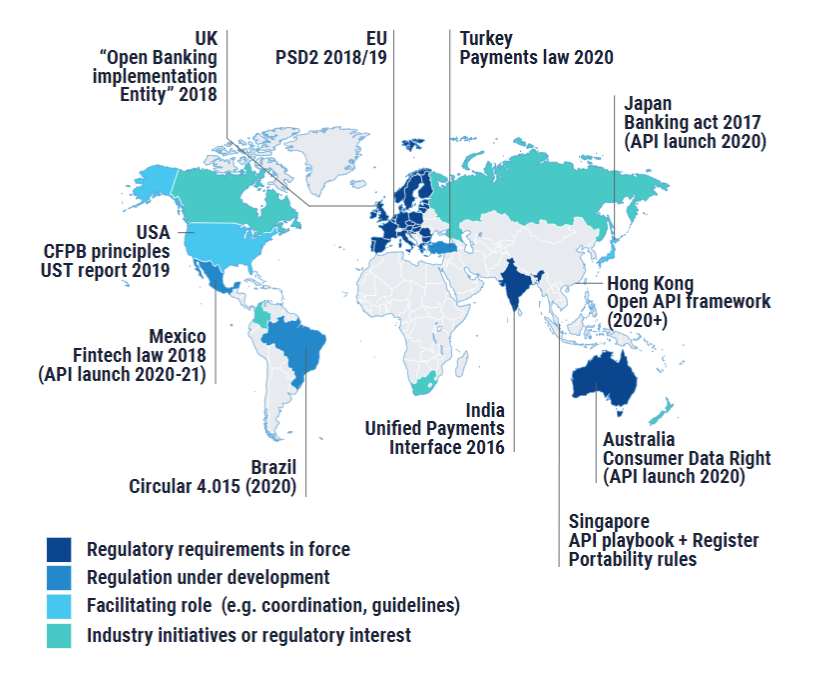
The Future of Regulation: The step change facing Open Banking
Regulators around the world are grappling with how to handle the new and rapidly evolving world of open finance and its associated technologies.
Lack of clarity: There is currently a lack of clarity around the regulatory environment for open finance, with different countries taking different approaches. This creates uncertainty for market participants and can discourage investment and innovation in the space.
Balancing innovation and consumer protection: Regulators are tasked with balancing the need to promote innovation in open finance with the need to protect consumers. This can be a difficult balance to strike, as new financial products and services may have unknown risks that need to be addressed.
Cross-border issues: Open finance operates globally, which means that regulatory issues often cross borders. This can make it challenging for regulators to enforce rules and protect consumers, as different countries may have different regulatory frameworks.
Overall, regulation is a major challenge in the future of open finance. Finding the right balance between these two objectives will be key to the success of open finance.
3. DeFi
Open finance can be decentralized or centralized, but decentralization is a key principle of the open finance movement.
The growth of decentralized finance (DeFi) is one of the biggest trends in open finance.
Decentralization in open finance refers to the distribution of control and power of customers over financial services, products, and data.
DeFi refers to a growing ecosystem of financial applications built on blockchain technology that provides alternatives to traditional financial services, such as lending, borrowing, and insurance. Some examples such as Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, Polygon, Aave (open-source lending platform), etc

There are still, however, so many existing challenges of DeFi such as:
Lack of regulation (previous part)
Security concerns: Decentralized platforms and smart contracts can be vulnerable to hacking, fraud, and other security threats. Example as (1) Immutable code: Once a smart contract is deployed on a blockchain, its code is immutable, meaning that it cannot be changed. This makes it difficult to fix bugs or vulnerabilities that may exist in the code. Or (2) No central authority: Decentralized platforms and smart contracts are designed to operate without a central authority. While this provides many benefits, it also means that there is no central authority to address security threats or recover lost funds.
Complexity: Open finance can be difficult to understand, especially for people who are new to cryptocurrencies and decentralized finance. This complexity can make some people hesitant to use these services.
That being said, it is important to note that the decentralized finance ecosystem is still in its early stages*, and there are **efforts underway to address these concerns and make these services more accessible, secure, and user-friendly.*
Additionally, as more people become familiar with open finance, it is likely that trust in these services will increase and DeFi is definitely one of the biggest trends in open finance
Overall, the future for open finance is very promising, as it has the potential to bring many benefits to consumers and the financial sector. As the trend towards open finance continues to grow, it will be important to monitor and understand its impact and to work together to ensure that it is developed and adopted in a responsible and sustainable manner.
